The Importance of Carotid Artery Stenting for Stroke Prevention
Introduction
Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death worldwide. Carotid artery stenting (CAS) is a vital procedure that can significantly reduce the risk of stroke in patients with carotid artery disease. This blog explores the importance of CAS, its procedure, benefits, and potential risks, highlighting why it is a critical intervention for stroke prevention.
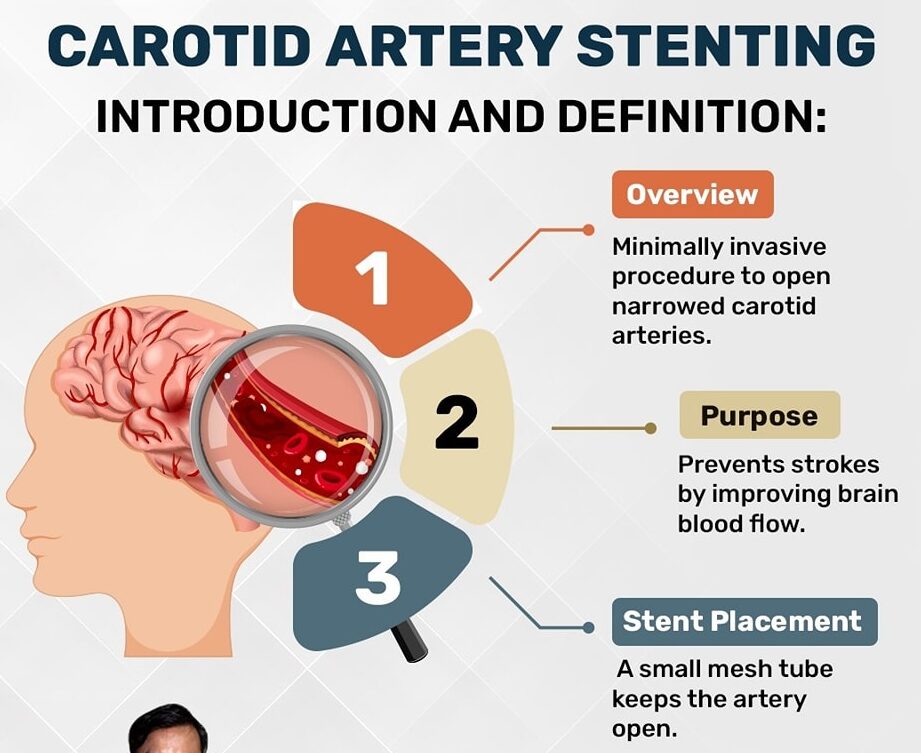
What is Carotid Artery Stenting?
Carotid artery stenting is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open narrowed carotid arteries. These arteries supply blood to the brain, and when they become narrowed due to plaque buildup, the risk of stroke increases. During CAS, a small mesh tube called a stent is placed in the artery to keep it open and ensure proper blood flow.
Why is Carotid Artery Stenting Important?
Stroke Prevention:
By opening the narrowed arteries, CAS helps prevent strokes, which can be debilitating or fatal.
Minimally Invasive:
Unlike traditional surgery, CAS is less invasive, leading to shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
Effective Alternative:
For patients who are not candidates for carotid endarterectomy (a surgical procedure), CAS offers an effective alternative.
Improved Quality of Life:
By reducing the risk of stroke, CAS can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life and overall health.
The Procedure
Preparation:
Patients are given local anesthesia, and a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery in the groin.
Stent Placement:
The catheter is guided to the carotid artery, where a balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and the stent is placed to keep it open.
Completion:
The catheter is removed, and the patient is monitored for a few hours before being discharged.
Benefits
Reduced Stroke Risk:
CAS significantly lowers the risk of stroke in patients with severe carotid artery stenosis.
Quick Recovery:
Patients typically recover faster compared to those undergoing surgical procedures.
Less Pain:
The minimally invasive nature of CAS results in less pain and discomfort.
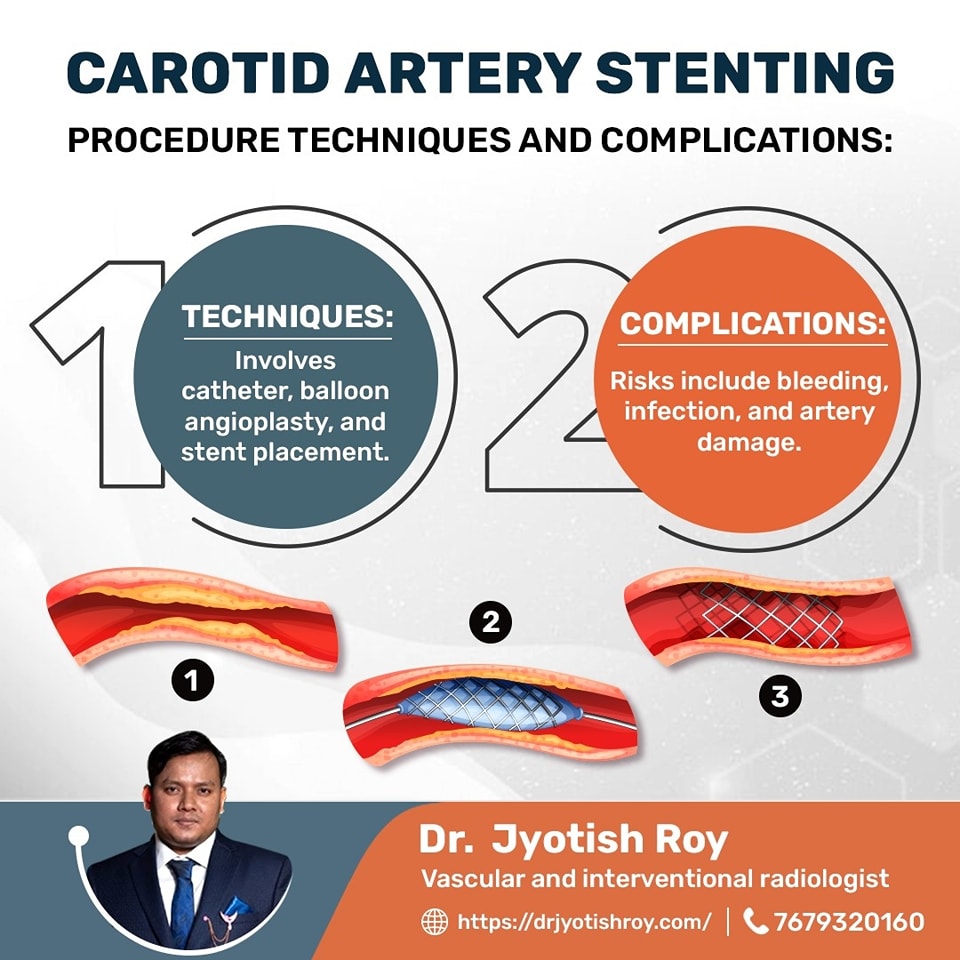
Risks and Complications
Bleeding:
There is a risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site.
Infection:
As with any procedure, there is a risk of infection.
Stroke During Procedure:
Although rare, there is a small risk of stroke during the procedure.
Artery Damage:
The procedure can potentially damage the artery.
Post-Procedure Care
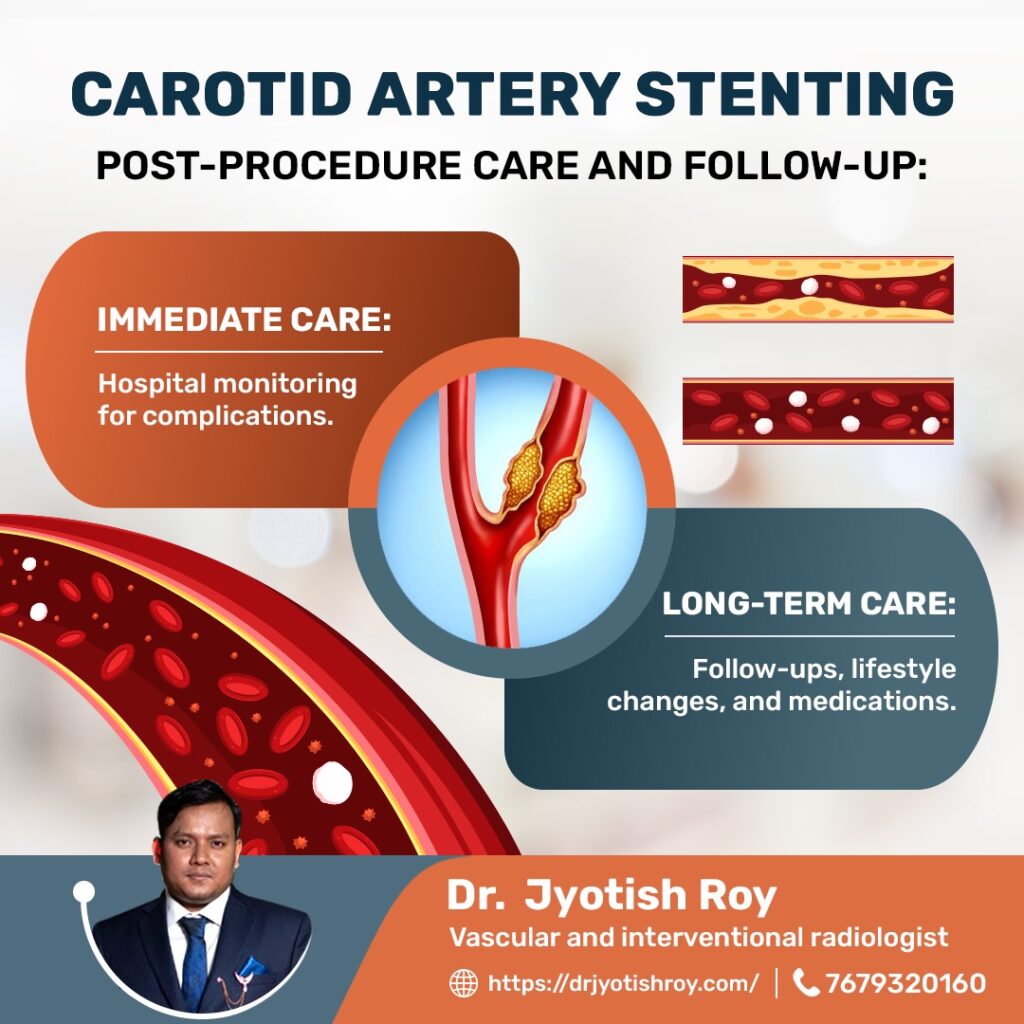
Monitoring:
Patients are monitored for any immediate complications.
Medications:
Blood-thinning medications are prescribed to prevent blood clots.
Lifestyle Changes:
Patients are advised to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise.
Follow-Up:
Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the stent and overall artery health.
Conclusion
Carotid artery stenting is a crucial procedure for preventing strokes in patients with carotid artery disease. Its minimally invasive nature, combined with its effectiveness in reducing stroke risk, makes it an essential intervention. If you or a loved one is at risk of stroke due to carotid artery stenosis, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the potential benefits of carotid artery stenting.
